Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Seiya*; Kawahara, Jun*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Sugihara, Kenta; Takase, Shinsuke*; Moriguchi, Shuji*; Hashimoto, Hirotada*
Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 17(1), p.2211143_1 - 2211143_23, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.52(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In tsunami inundations or slope disasters of heavy rain, a lot of floating debris or driftwood logs are included in the flows. The damage to structures from solid body impacts is more severe than the damage from the water pressure. In order to study free-surface flows that include floating debris, developing a high-accurate simulation code of free-surface flows with high performance for large-scale computations is desired. We propose the single-phase free-surface flow model based on the cumulant lattice Boltzmann method coupled with a particle-based rigid body simulation. The discrete element method calculates the contact interaction between solids. An octree-based AMR (Adaptive Mesh Refinement) method is introduced to improve computational accuracy and time-to-solution. High-resolution grids are assigned near the free surfaces and solid boundaries. We conducted two kinds of tsunami flow experiments in the 15 and 70 m water tanks at Hachinohe Institute of Technology and Kobe University to validate the accuracy of the proposed model. The simulation results have shown good agreement with the experiments for the drifting speed, the number of trapped wood pieces, and the stacked angles.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Aoki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Hiromichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Parallel Computing, 108, p.102851_1 - 102851_12, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.94(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)The aerodynamics simulation code based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) using forest-of-octrees-based block-structured local mesh refinement (LMR) was implemented, and its performance was evaluated on GPU-based supercomputers. We found that the conventional Space-Filling-Curve-based (SFC) domain partitioning algorithm results in costly halo communication in our aerodynamics simulations. Our new tree cutting approach improved the locality and the topology of the partitioned sub-domains and reduced the communication cost to one-third or one-fourth of the original SFC approach. In the strong scaling test, the code achieved maximum 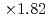 speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
Asahi, Yuichi; Hatayama, Sora*; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (IEEE Cluster 2021) (Internet), p.686 - 691, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.38(Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture)We develop a convolutional neural network model to predict the multi-resolution steady flow. Based on the state-of-the-art image-to-image translation model pix2pixHD, our model can predict the high resolution flow field from the set of patched signed distance functions. By patching the high resolution data, the memory requirements in our model is suppressed compared to pix2pixHD.
Hemmi, Ko; Walker, A.*; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
Radiochimica Acta, 109(7), p.539 - 546, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Plutonium(IV) sorption onto quartz in carbonate solutions was systematically investigated under anaerobic conditions to analyze the sorption behaviors of Pu(IV) with a non-electrostatic model (NEM). Pu(IV) sorption data was obtained from batch sorption experiments as a function of pH and carbonate concentration. The Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz showed similar tendencies to Th(IV), which is considered to be chemically analogous as a tetravalent actinoid. The distribution coefficient,  d, of Pu(IV) onto quartz showed inverse proportionality to the square of the total carbonate concentration under the investigated pH conditions of 8 to 11. The modeling study, however, revealed a Th(IV) sorption model, which is
d, of Pu(IV) onto quartz showed inverse proportionality to the square of the total carbonate concentration under the investigated pH conditions of 8 to 11. The modeling study, however, revealed a Th(IV) sorption model, which is  SOTh(OH)
SOTh(OH)
 and
and  SOThOH(CO
SOThOH(CO )
)
 , could not be applied to simulate the Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz. It was inferred that the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged ligands limited the formation of
, could not be applied to simulate the Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz. It was inferred that the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged ligands limited the formation of  SOM(OH)
SOM(OH)
 and
and  SOMOH(CO
SOMOH(CO )
)
 for Pu(IV) with smaller ionic radii than Th(IV). The Pu(IV) sorption model was developed as
for Pu(IV) with smaller ionic radii than Th(IV). The Pu(IV) sorption model was developed as  SOPu(OH)
SOPu(OH) and
and  SOPu(OH)
SOPu(OH)
 . In addition, data of Pu(IV) sorption onto muscovite was obtained in order to be compared with data for quartz.
. In addition, data of Pu(IV) sorption onto muscovite was obtained in order to be compared with data for quartz.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Technology 2015-044, 20 Pages, 2016/03
In order to estimate public dose under a criticality accident in fuel solution of a fuel reprocessing plant, release behavior of radioiodine from the fuel solution to atmosphere is very important. In this report, time evolution of  I concentration in gas phase of TRACY core tank was measured until the concentration in the solution decreased. Furthermore, cumulative release ratio (CRR) and release rate (RR) from the solution to the atmosphere of radioiodine were evaluated by applying previously-reported evaluation model. As a result, for the case of short transient criticality, RR of
I concentration in gas phase of TRACY core tank was measured until the concentration in the solution decreased. Furthermore, cumulative release ratio (CRR) and release rate (RR) from the solution to the atmosphere of radioiodine were evaluated by applying previously-reported evaluation model. As a result, for the case of short transient criticality, RR of  I became maximum at 1 hour later from the ending and almost constant after 8 hour later. Furthermore, relationship of each elapsed time between total fission number and release rate of
I became maximum at 1 hour later from the ending and almost constant after 8 hour later. Furthermore, relationship of each elapsed time between total fission number and release rate of  I could be derived. On the other hand, for the case of long criticality excursion, such as JCO criticality accident, the CRR and RR of radioiodine increased monotonously with time.
I could be derived. On the other hand, for the case of long criticality excursion, such as JCO criticality accident, the CRR and RR of radioiodine increased monotonously with time.
Katayama, Kazunari*; Ushida, Hiroki*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Goto, Minoru; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
Fusion Science and Technology, 68(3), p.662 - 668, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:79.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium production utilizing nuclear reactions by neutron and lithium in a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor is attractive for development of a fusion reactor. From viewpoints of tritium safety and production efficiency, tritium confinement technique is an important issue. It is known that alumina has high resistance for gas permeation. In this study, hydrogen permeation experiments in commercial alumina tubes were conducted and hydrogen permeability, diffusivity and solubility was evaluated. By using obtained data, tritium permeation behavior from an Al O
O -coated Li-compound particle was simulated. Additionally, by using literature data for hydrogen behavior in zirconium, an effect of Zr incorporation into an Al
-coated Li-compound particle was simulated. Additionally, by using literature data for hydrogen behavior in zirconium, an effect of Zr incorporation into an Al O
O coating on tritium permeation was discussed. It was indicated that the majority of produced tritium was released through the Al
coating on tritium permeation was discussed. It was indicated that the majority of produced tritium was released through the Al O
O coating above 500
coating above 500 C. However, it is expected that total tritium leak is suppressed to below 0.67% of total tritium produced at 500
C. However, it is expected that total tritium leak is suppressed to below 0.67% of total tritium produced at 500 C by incorporating Zr fine particles into the inside of Al
C by incorporating Zr fine particles into the inside of Al O
O coating.
coating.
 -mode plasmas in JT-60U tokamak
-mode plasmas in JT-60U tokamakUrano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kamada, Yutaka
Nuclear Fusion, 46(8), p.781 - 787, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:58.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The degradation of energy confinement with increased toroidal beta 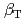 was shown by the non-dimensional analysis in JT-60U. The dependence of the energy confinement on
was shown by the non-dimensional analysis in JT-60U. The dependence of the energy confinement on 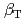 was examined by both the JT-60U ELMy
was examined by both the JT-60U ELMy 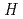 -mode confinement database and the dedicated experiment on a single
-mode confinement database and the dedicated experiment on a single 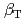 scan while
scan while 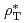 and
and 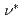 were kept fixed as well as the other magnetic geometrical parameters. In both cases, the degradation of energy confinement with increasing
were kept fixed as well as the other magnetic geometrical parameters. In both cases, the degradation of energy confinement with increasing 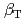 was observed, satisfying the relation of
was observed, satisfying the relation of 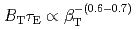 . This dependence is a little weaker than that predicted by the IPB98(y,2) scaling. The fusion power production rate was estimated to increase in proportion to
. This dependence is a little weaker than that predicted by the IPB98(y,2) scaling. The fusion power production rate was estimated to increase in proportion to 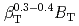 .
.
Takizuka, Tomonori; Urano, Hajime; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(6), p.799 - 806, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of the ELMy H-mode confinement on the beta has been investigated for a long time, but a common conclusion has not yet been obtained.The IPB98(y,2) scaling shows a strong degradation with beta, while DIII-D and JET experiments exhibited the absence of the beta degradation. Recent JT-60U experiment demonstrated that the strong beta degradation really exists for the ELMy H-mode. In the present paper, we analyze the JT-60U ELMy H-mode confinement database and confirm the strong power degradation of the confinement time, which corresponds to the strong beta degradation consistent with the above result. We analyze also the ITPA H-mode confinement database in detail. How the beta dependence of the confinement time is changed by the externally given parameters, such as the shape parameters, are investigated.
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Stober, J.*; Lomas, P. J.*; Saibene, G.*; Andrew, Y.*; Belo, P.*; Conway, G. D.*; Herrmann, A.*; Horton, L. D.*; Kempenaars, M.*; Koslowski, H.-R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(11), p.1213 - 1223, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:76.37(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(10), p.S13 - S31, 2005/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper summarizes the results presented at the 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference 2004 in the sessions of confinement, plasma-wall interaction and innovative confinement concept. The highlights of the presentations are as follows. Long pulse operation with high beta and high bootstrap fraction much longer than the current diffusion time has been achieved. The discharge scenario optimization and its extrapolation towards ITER have progressed remarkably. Significant progress has been made in understanding of global confinement and transport physics.
 and collisionality approaching ITER conditions
and collisionality approaching ITER conditionsCordey, J. G.*; Thomsen, K.*; Chudnovskiy, A.*; Kardaun, O. J. W. F.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Snipes, J. A.*; Greenwald, M.*; Sugiyama, L.*; Ryter, F.*; Kus, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(9), p.1078 - 1084, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:82.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The condition of the latest version of the ELMy H-mode database has been re-examined. It is shown that there is bias in the ordinary least squares regression for some of the variables. To address these shortcomings three different techniques are employed: (a)principal component regression, (b)an error in variables technique and (c)the selection of a better conditioned dataset with fewer variables. Scalings in terms of the dimensionless physics valiables, as well as the standard set of engineering variables, are derived. The new scalings give a very similar performance for existing scalings for ITER at the standard beta, but a much improvement performance at higher beta.
Ueda, Yoshio*; Inoue, Takashi; Kurihara, Kenichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 46(12), p.845 - 852, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Oyama, Naoyuki; Miura, Yukitoshi; Hubbard, A. E.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(11), p.1745 - 1755, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.22(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent experiments in the JFT-2M tokamak have concentrated on the studies of the access condition for the H-mode operation without any large ELMs, namely High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode regime in terms of the pedestal parameters. The HRS regime is more likely at the higher edge density and lower edge temperature, while the ELMy H-mode having large ELMs appears at the lower edge density and higher edge temperature. It is found that the ELMy/HRS operational boundary occurs at the normalized electron collisionality of  *
*
 1 in the plasma edge region, depending slightly on q
1 in the plasma edge region, depending slightly on q . A key feature of the HRS H-mode is the presence of the coherent magnetic fluctuations in the frequency range of the order of 10-100 kHz. It is suggested that the edge MHD activities may keep an edge pressure below a certain level needed to induce a large ELM.
. A key feature of the HRS H-mode is the presence of the coherent magnetic fluctuations in the frequency range of the order of 10-100 kHz. It is suggested that the edge MHD activities may keep an edge pressure below a certain level needed to induce a large ELM.
Shimada, Michiya; Campbell, D.*; Stambaugh, R.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Costley, A. E.*; Donn , A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
, A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
This paper summarises recent progress in the physics basis and its impact on the expected performance of ITER. Significant progress has been made in many outstanding issues and in the development of hybrid and steady state operation scenarios, leading to increased confidence of achieving ITER's goals. Experiments show that tailoring the current profile can improve confinement over the standard H-mode and allow an increase in beta up to the no-wall limit at safety factors  4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of
4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of  12MA, high Q
12MA, high Q  10 and long pulse (
10 and long pulse ( 1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
Huang, X.*; Mashimo, Tsutomu; Ono, Masao; Tomita, Takeshi; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Mori, Nobuo*
Journal of Applied Physics, 96(3), p.1336 - 1340, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:42.77(Physics, Applied)Mega-gravity field experiments were performed on the Bi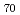 Sb
Sb (atomic percent) alloy and pure Bi below their melting points, to investigate the change in crystalline state. For the alloy centrifuged at 191-205
(atomic percent) alloy and pure Bi below their melting points, to investigate the change in crystalline state. For the alloy centrifuged at 191-205  C, no change in composition was observed, and the grain sizes of the crystals decreased from several mm to tens of
C, no change in composition was observed, and the grain sizes of the crystals decreased from several mm to tens of  m, while no distinct change in grain size was observed for the centrifuged pure Bi. The alloy centrifuged at 220-240
m, while no distinct change in grain size was observed for the centrifuged pure Bi. The alloy centrifuged at 220-240  C consisted of two regions with different morphologies-fine-grained crystals with grain sizes around tens of
C consisted of two regions with different morphologies-fine-grained crystals with grain sizes around tens of  m in the low gravity region, and large crystals with grain sizes several mm long and hundreds of
m in the low gravity region, and large crystals with grain sizes several mm long and hundreds of  m wide along the direction of gravity in the high gravity region, where sedimentation of atoms was confirmed. The large crystals with hexagonal structures were formed by preferential crystal growth roughly along the c axes, and a large strain that increased as the gravitational field increased existed inside these crystals. Formation of this anomalous crystal state might be correlated with the sedimentation of atoms.
m wide along the direction of gravity in the high gravity region, where sedimentation of atoms was confirmed. The large crystals with hexagonal structures were formed by preferential crystal growth roughly along the c axes, and a large strain that increased as the gravitational field increased existed inside these crystals. Formation of this anomalous crystal state might be correlated with the sedimentation of atoms.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Bakhtiari, M.; Kasai, Satoshi; Kawashima, Hisato; Kusama, Yoshinori; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(5A), p.A157 - A163, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:56.48(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A new operating regime, High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode regime, has been discovered on JFT-2M, which is easily reproduced under the wall fueling from the boronized first wall. Accompanying the HRS H-mode transition, the coherent magnetic and floating potential fluctuations are seen on magnetic probes at vessel wall and Langmuir probe in SOL, respectively. These coherent fluctuations have a frequency of the order of 10-100 kHz with significant variation, which is recognized to be important to enhance the particle transport. The HRS can be seen even at 

 3 with
3 with 
 /
/
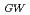
 0.4 for the fixed delta
0.4 for the fixed delta 0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta
0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta 0.75 and
0.75 and 

 2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta
2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta 0.3 with moderate
0.3 with moderate 

 4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of
4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of 
 /
/
 0.4.
0.4.
Li, J.; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physics of Plasmas, 11(4), p.1493 - 1510, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:85.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The electron temperature gradient (ETG) driven turbulence in tokamak core plasmas is numerically investigated based on three-dimensional gyrofluid model with adiabatic ion response. Attentions are focused on the zonal flow dynamics in ETG fluctuations and the resultant electron heat transport. A high electron energy confinement mode is found in the weak magnetic shear regime, which is closely relevant with self-organization behavior of turbulence through the enhanced zonal flow dynamics rather than the weak shear stabilization of ETG fluctuations. It is demonstrated that the weak shear is favorable for the enhancement of zonal flows in ETG turbulence.
JT-60 Team
JAERI-Review 2003-029, 197 Pages, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Kubo, Hirotaka; Sakurai, Shinji; Higashijima, Satoru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Itami, Kiyoshi; Konoshima, Shigeru; Nakano, Tomohide; Koide, Yoshihiko; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316(1-3), p.1197 - 1201, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English